What is Implementation Science?
|
Implementation science (IS) is the study of implementing (putting into effect) proven evidence-based interventions across a range of healthcare settings. Implementation science may also be called dissemination and implementation research (D&I Research). The field of implementation science falls under the broader category of health services research (HSR).
Why is implementation science needed?Studies have shown that variations in clinical practice often lead to suboptimal care, especially when clinicians deviate from evidence-based practice guidelines. Implementation science addresses the gaps between the interventions that research have shown to be effective and the dissemination and delivery of those interventions into practice.
|
It takes an average of 17 years for only 14% of research to get integrated into clinical practice...
Balas EA. From appropriate care to evidence-based medicine. Pediatr Ann. 1998 Sep;27(9):581-4.
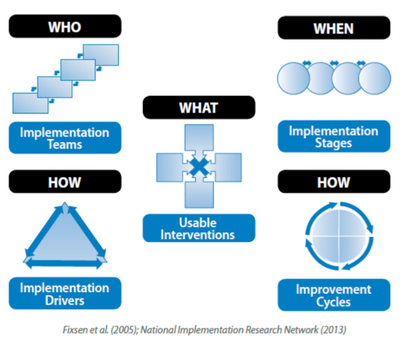
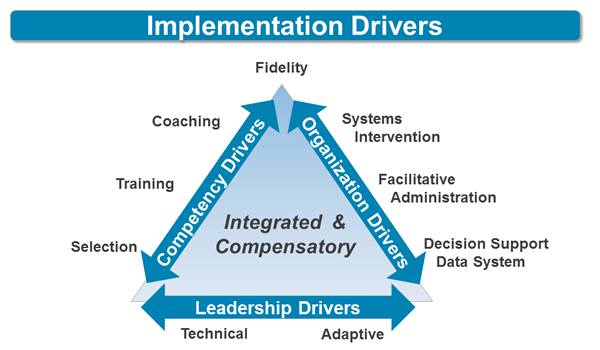
National Implementation Research Network (NIRN) at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
Implementation science is the scientific study of variables and conditions that impact changes at practice, organization, and systems levels; changes that are required to promote the systematic uptake, sustainability and effective use of evidence-based programs and practices in typical service and social settings.
Implementation science is the scientific study of variables and conditions that impact changes at practice, organization, and systems levels; changes that are required to promote the systematic uptake, sustainability and effective use of evidence-based programs and practices in typical service and social settings.
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR)
The CFIR provides a menu of constructs that have been associated with effective implementation. Those constructs fall under the following domains:
The CFIR provides a menu of constructs that have been associated with effective implementation. Those constructs fall under the following domains:
- Intervention Characteristics
- Outer Setting
- Inner Setting
- Characteristics of Individuals
- Process
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Implementation science is the study of methods to promote the integration of research findings and evidence into healthcare policy and practice. It seeks to understand the behavior of healthcare professionals and other stakeholders as a key variable in the sustainable uptake, adoption, and implementation of evidence-based interventions. As a newly emerging field, the definition of implementation science and the type of research it encompasses may vary according setting and sponsor. However, the intent of implementation science and related research is to investigate and address major bottlenecks (e.g. social, behavioral, economic, management) that impede effective implementation, test new approaches to improve health programming, as well as determine a causal relationship between the intervention and its impact.
Clinical and Translational Science Institute (CTSI) at UCSF
Implementation scientists draw on a range of theories and methods to determine which factors promote or impede the adoption, adaptation, and maintenance of specific health-related interventions by individuals, health providers, insurers, policy makers, and communities. Direct engagement with the institutions and communities where health interventions are introduced is a key element of implementation science research.
Center for Research in Implementation Science and Prevention (CRISP) at the University of Colorado
Implementation science is the study of methods that influence the integration of evidence-based interventions into practice settings. Dissemination is the process of spreading knowledge and information to these settings.
- Implementation science seeks to understand the barriers and facilitators that influence successful implementation of effective interventions.
- Translating research into practice is a complex process that involves: disseminating the information to clinicians, clinicians adopting the program and successfully implementing it into their setting, and the sustainability of the intervention.
- Implementation science enhances the extent to which intervention research is generalizable, representative, and comprehensive in order to increase public health impact.
- To address complex health issues, researchers, clinicians and communities need to work together and share their knowledge and expertise to increase the number of evidence-based interventions that are implemented in real-world practices.
- We need more creative and rigorous dissemination efforts, beyond journal publications and meeting presentations, to increase the number of evidence-based interventions that are implemented in real-world practices.
Global Alliance for Chronic Diseases (GACD)
Implementation science is commonly defined as the study of methods and strategies to promote the uptake of interventions that have proven effective into routine practice, with the aim of improving population health. Implementation science therefore examines what works, for whom and under what circumstances, and how interventions can be adapted and scaled up in ways that are accessible and equitable. A commonly used definition of implementation research is that it is the scientific study of methods to promote the systematic uptake of research findings and other evidence-based practices into routine practice, and, hence, to improve the quality and effectiveness of health services and care.
Dissemination and implementation (D&I) research seeks to understand how to best apply scientific advances in the real world, by focusing on pushing the evidence-based knowledge base out into routine use. (from Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health: Translating Science to Practice by Ross C. Brownson, Graham A. Colditz, and Enola K. Proctor)
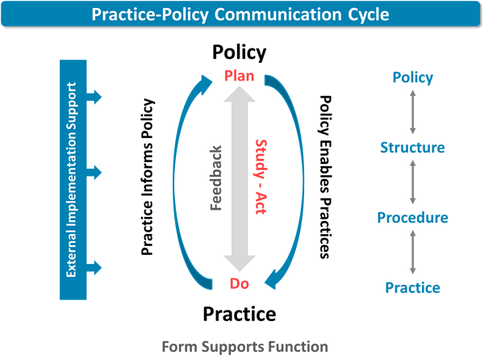
How does implementation science (IS) fit into CME/CE and quality improvement (QI)?
CME/CE providers can apply the principles of implementation science (IS) and find practical and effective ways to put clinical education into action. The application of implementation science becomes the framework for achieving sustainable systems-level quality improvement (QI), especially when the practice-policy loops are closed effectively.
CME = continuing medical education
CE = continuing education
IS = implementation science
QI = quality improvement
CME = continuing medical education
CE = continuing education
IS = implementation science
QI = quality improvement
More information about implementation science can be found at the Active Implementation Hub, which is developed and maintained by the State Implementation and Scaling-up of Evidence-based Practices Center (SISEP) and the National Implementation Research Network (NIRN) at The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill's FPG Child Development Institute.
Q Synthesis LLC
Advancing interprofessional collaborative practice by applying principles of systems thinking, implementation science, and health services research
Advancing interprofessional collaborative practice by applying principles of systems thinking, implementation science, and health services research
|
Q Synthesis LLC
13 Summit Square Ctr #143 Langhorne, PA 19047 Phone: (215) 867-9122 Fax: (888) 409-9721 Email: [email protected] |
Sign up to receive updates:
|