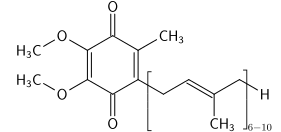
|
Q Synthesis LLC is not a biotechnology company involved in the synthesis of coenzyme Q. However, the topic of coenzyme Q brings up some memories from organic chemistry. It's Fun Friday, so let's spend a few minutes diving into this interesting topic. Coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, coenzyme Q10, or CoQ is chemical compound that is synthesized within the body. We study about coenzyme Q in biochemistry, and here's what CoQ looks like: Coenzyme Q can exist in three oxidation states: (1) the fully reduced ubiquinol form (CoQ10H2), (2) the radical semiquinone intermediate (CoQ10H·), and (3) the fully oxidized ubiquinone form (CoQ10).
CoQ works in mitochondria where energy (ATP) is generated. Organs like the heart, liver, and kidney have the highest concentrations of CoQ. The biosynthesis of CoQ involves an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase. Given that statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, some researchers are exploring how statins may impact levels of CoQ. There are many other steps and scientists continue to work on mapping out CoQ biosynthesis, metabolism, and transport pathways. In summary, coenzyme Q is a fascinating topic and I'm sure we'll be hearing more about CoQ as researchers examine the clinical impact of CoQ dietary supplements and continue to gain a deeper understanding of CoQ biosynthesis. Laredj LN, Licitra F, Puccio HM. The molecular genetics of coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochimie. 2014 May;100:78-87. Tran UC, Clarke CF. Endogenous Synthesis of Coenzyme Q in Eukaryotes. Mitochondrion. 2007;7(Suppl):S62-S71. Caso G, Kelly P, McNurlan MA, Lawson WE. Effect of coenzyme q10 on myopathic symptoms in patients treated with statins. Am J Cardiol. 2007 May 15;99(10):1409-12. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Acosta MJ, Vazquez Fonseca L, Desbats MA, Cerqua C, Zordan R, Trevisson E, Salviati L. Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Aug; 1857(8):1079-1085. Comments are closed.
|
Author@DrJosephKim Sign up to receive updates:
|